Finally, a new release!
Blender includes production ready camera and object tracking. Allowing you to import raw footage, track the footage, mask areas and see the camera movements live in your 3D scene. Eliminating the need to switch between programs. Auto and Manual tracking Powerful camera reconstruction Real-time preview of your tracked footage and 3D scene. The iconic Blender Open Movies. Featuring all the production files, assets, artwork, and never-seen-before content. Having done so, you can now manipulate the camera using the same tools that are used to transform any object: Roll. Press R to enter object rotation mode. The default will be to rotate the camera in its local Z axis (the axis orthogonal to the camera view), which is the definition of a camera 'roll'. Vertical Pan or Pitch.
- Pixel Plow's outsourced rendering service enables you to seamlessly render offsite. Render online with the power of cloud rendering. Pixel Plow supports most render applications like 3D Studio Max, 3dsmax, Maya, Terragen, Houdini, Lightwave, Modo, Cinema 4D, C4D, Cinema4D, LuxRender, Blender, Maxwell Render, Vue, and more.
- Next up, Carlos teaches you the basics of animation with Blender so you can give life to the objects you have created. See how the armatures, keyframes, timeline, and graph editor work. Then, discover how to set up a 3D camera and how it works together with other 2D animated objects.
There are many fixes, and many improvements, and also, many new features
this list is not really showing pictures, and also not everything that is in the release, but now, there are more people cooperating on the docs so I hope, the pictures will make it soon to the wiki pages which now grow quite fast on the Github wiki: https://github.com/vilemnovak/blendercam/wiki
big thanks for the wiki go to Jeff Doyle,who started this new documentation project.
larger features
| V-carve test by Jeff Doyle |
- Polygon library was replaced with shapely library completely. This was a huge task, touching almost all areas of blender CAM.
- OpenCAMlib support by Karol Suprynowicz
- manual bridges placement - now you can define bridges with a group of curves.
- auto bridges placement was improved
- medial axis strategy - you can use this for V-carving and Ball-carving(not sure if that's the right name, but enables you to use the ball cutter for the same task).
- projecte curve strategy - this is a complex strategy that enables undercuts. Some docs will be needed.
- Intarsion tool modifies curves to be suitable for intarsion - the resulting shape can be cut inside/outside and will fit.
- Overcuts tool - this is experimental, adds simple overcuts to the curve object, good for fast setting up of slots.
- several new postprocessors, most of them by new contributors!
- 4 axis code is enabled in experimental features, but it's still heavy WIP, and is released mainly to get more people communicating about it!
small features:
- experimental features can be switched off in addon preferences.
- curve remove doubles operator
- Denver Hull commited a patch which adds operation start-stop points and fixed some unit problems
BIG THANKS
to all contributors, to people who communicated on the forums, who helped by donating money, to anybody using blender CAM :)
and SORRY to those I forgot to mention here. And to those to whose e-mails I forgot to reply..
Enjoy using BlenderCAM and stop by on github on the forum to let us know about bugs or your ideas.
The Camera view shows the current scene as seen from the currently active camera's view point.
The Camera view can be used to virtually compose shots and preview how the scene will look when rendered.The rendered image will contain everything within the dashed line.
See also
Camera Settings for details how camera settings are used for display & rendering.
Hint
The active camera can be selected while in camera view using the camera frame(assuming the object isn't hidden). Can you pirate fl studio.
Blender Camera Lock
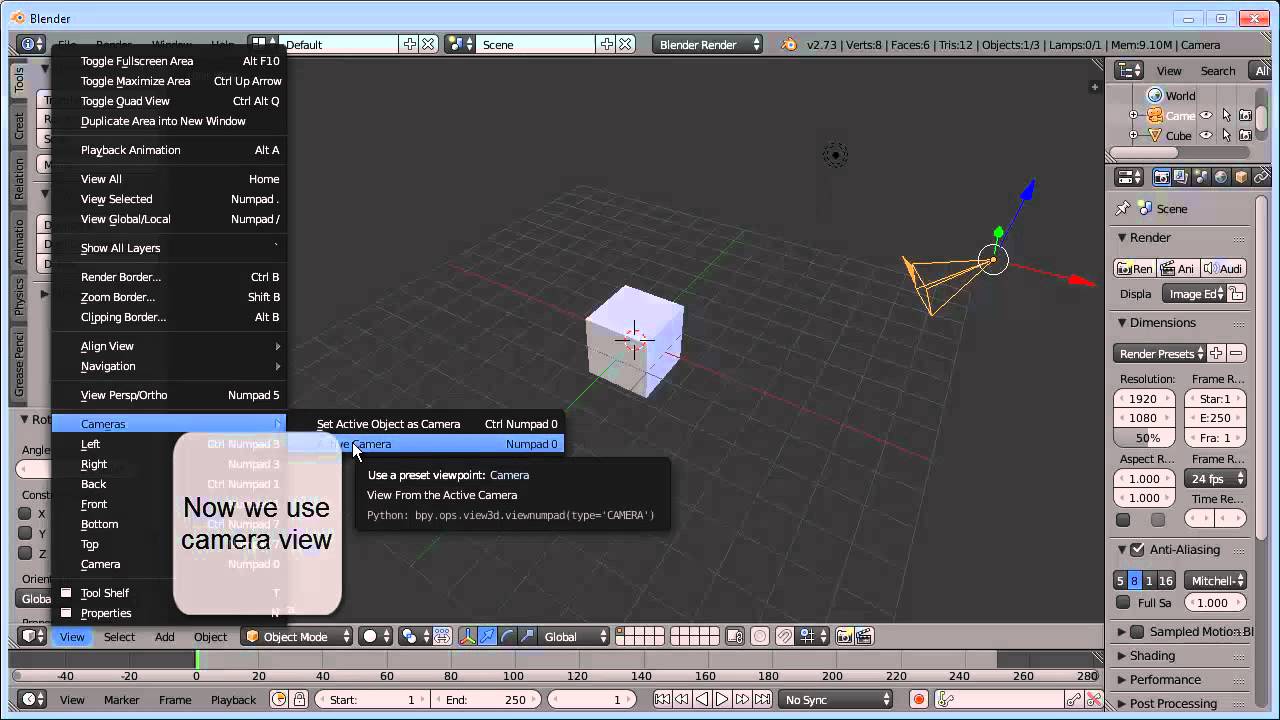
Viewing the Active Camera¶
Reference
All modes Text note online.
Animal crossing lets go to the city wii u. View ‣ Cameras ‣ Active Camera
Numpad0
This switches the view to the active camera.The triangle above the camera will become shaded when active.
Setting the Active Camera¶
Reference
Object Mode
View ‣ Cameras ‣ Set Active Object as Camera
Ctrl-Numpad0
Active camera (left) displayed with a solid triangle above it.¶
This is the camera currently used for rendering and when viewing from the camera.
This sets the current active object as the active camera & switches to the camera view.
The active camera can also be set in the Scene tab of the Properties.
Note
The active camera, as well as the layers, can be specific to a given view,or global (locked) to the whole scene.See Local Camera.
Animated Camera Switching¶
By default a scene contains one camera. However, a scene can contain more than one camera,but only one of them will be used at a time.So you will only need to add a new camera if you are making cuts between them.See Animating Cameras.
Frame Camera Bounds¶
Reference
All Modes
View ‣ Cameras ‣ Frame Camera Bounds
Home
Centers the camera view inside the 3D Viewport's screen areaand resizes the view to fit within the area's bounds.
Camera Navigation¶
There are several different ways to navigate and position the camera in your scene,some of them are explained below.
Zooming in and out is possible in this view, but to change the viewpoint,you have to move or rotate the camera.
Hint
The active 'camera' might be any kind of object.So these actions can be used, for example, to position and aim a light.
Move Active Camera to View¶
This matches the active camera to a regular (non camera) view,for a convenient method of placing the camera without having to move the object directly.
Camera View Positioning¶
By enabling Lock Camera to View in the View panel of the Sidebar region,while in camera view, you can navigate the 3D Viewport as usual,while remaining in camera view. Controls are exactly the same as when normally moving in 3D.
See also
Fly/Walk Navigation for first person navigation that moves the active camera too.
Roll, Pan, Dolly, and Track¶
To perform these camera moves, the camera must first be selected so transform operations apply to it.The following actions also assume that you are in camera view.Having done so, you can now manipulate the camera using the same tools that are used to transform any object:
Press R to enter object rotation mode. The default will be to rotate the camera in its local Z axis(the axis orthogonal to the camera view), which is the definition of a camera 'roll'.
This is just a rotation along the local X axis. Press R to enter object rotation mode,then X twice (the first press selects the global axis,pressing the same letter a second time selects the local axis – this works with any axis;see the axis locking page).
Blender Camera Online Store
This corresponds to a rotation around the camera's local Y axis.Press R, and then Y twice.
To dolly the camera, press G then MMB (or Z twice).
Press G and move the mouse (you can use X twice or Yto get pure-horizontal or pure-vertical sideways tracking).
